Energy-saving doors and windows are a kind of doors and windows to increase the lighting and ventilation area or to show the character characteristics of modern buildings.
In order to increase the area of lighting and ventilation or show the character characteristics of modern buildings, the area of doors and windows of buildings is getting larger and larger, and the curtain wall of buildings with full glass, so that the heat loss of doors and windows accounts for more than 40% of the total heat loss of buildings, energy conservation of doors and windows is the key to building energy conservation. Doors and windows are not only sensitive parts of energy gains and losses, but also related to lighting, ventilation, sound insulation and facade modeling. This puts forward higher requirements for the energy saving of doors and windows. Its energy saving treatment is mainly to improve the thermal insulation performance of materials and the sealing performance of doors and windows.
In the development of Windows, balcony windows develop to the floor push-pull type, and develop new medium suspension and upper suspension windows; Toilet mainly develops ventilation windows, which have two functions of preventing sight and ventilation; kitchen windows will develop towards long windows, which will be located between kitchen wall cupboard and the operating table; Door and window shading technology is suitable for wide promotion in hot summer and warm winter areas.
The Ministry of Housing and Construction controls the energy-saving capacity of doors and windows by issuing building energy-saving design standards for five climate zones. Among them, the most important parameter limit is the upper limit of the heat transfer coefficient K of doors and windows. Every time the standard is refreshed, the upper limit of the K value will change to low; The second is the lower limit of the air tightness of doors and windows; The other is the shading coefficient, the lower the value, the less the radiation energy at home. The South pays more attention to the upper limit of this value.
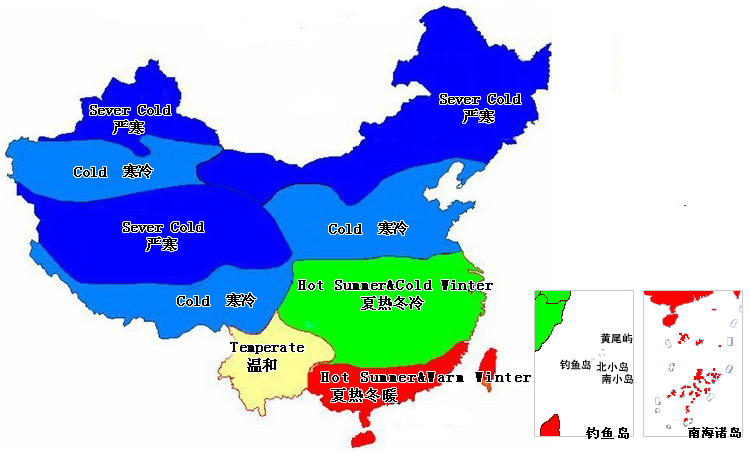
The latest version of the national standards (JGJ26) and areas with hot summer and cold winter (JGJ134) in cold and cold regions is 2010; The latest version in hot summer and warm winter regions (JGJ75) is 2003.
Other documents also have energy saving requirements. When GB/50189-2005 "design standard for energy saving of public buildings" was issued, in order to meet the low k value of doors and windows, pure aluminium windows became broken bridge aluminum with double glass hollow glass. Now the three climate zones have the standards of 2010 version of residential buildings, and the local standards are also spread out, so there are polyurethane doors and windows and three glass-aluminum composite windows. The old broken bridge aluminum is getting wider and wider. With complex heat insulation strips, plastic steel windows have begun to use other materials to improve in order to pass the air tightness requirements. Glass, single layer from 5mm (previously 4mm Main Force), white glass has been replaced with Low-E.
The principle is to reduce heat conduction (mainly reduce k value), reduce air convection (improve air tightness, reduce thermal expansion and contraction), and adjust household radiation (mainly refers to adjusting sunshade).
China is a big energy consuming country. In order to reduce energy consumption, the country has carried out many energy saving reforms. However, in the building envelope structure, the energy consumption of building doors and windows accounts for 49% of its energy consumption.
Building doors and windows are very weak in the thermal insulation performance of buildings. With the continuous improvement of people's living standards, in order to create a comfortable living environment, indoor refrigeration or mining methods are becoming more and more common, as one of the surface enclosure of buildings, doors and windows directly affect the energy saving Performance of Buildings. Improving the thermal insulation performance of doors and windows is the main way to ensure the energy consumption of buildings, nowadays, the use of energy-saving doors and windows in building energy conservation has attracted more and more attention.
Real energy saving system
The real energy-saving system doors and windows are not simply broken bridge aluminum profiles or Low-E hollow glass. It is a perfect combination of systems, and the comprehensive results of each link performance are indispensable, three main factors should be considered to measure whether building doors and windows are energy-saving, namely, convection of heat, conduction of heat and radiation of heat:
Heat loss is the circulation flow of hot and cold air through the gap between doors and windows, and heat exchange through gaseous exchange, resulting in heat loss;
Heat conduction is the heat transfer by the molecular movement of the materials used by doors and windows, which is transmitted to the other through one side of the material itself, resulting in heat loss;
Radiation is mainly transmitted directly in the form of radiation, resulting in energy loss.
From the above three elements, we should pay attention to the following aspects for real energy-saving doors and windows:
Design and selection of profiles
First of all, different profiles have different performance, mainly because different heat-conduction coefficient determines the energy consumption of doors and windows. When you choose a material, it is very important to design the section of the profile.
The heat insulation strips on the frame and fan material are not on the same side (by outdoor or indoor), so that after the hardware accessories are installed, the indoor and outdoor profiles are connected to each other through metal hardware accessories bypassing the heat insulation strips, thus making the heat transfer quickly, affect the energy saving performance of doors and windows, etc.
Glass selection
We know that energy loss is mainly caused by convection, conduction and radiation. Glass is mainly heat radiation energy loss, so when we choose the glass of building doors and windows, we must reasonably choose glass to ensure the energy saving of the whole building. In terms of the southern region, the southern region belongs to the hot summer and warm winter region, with a long period of high temperature. In terms of glass selection, transparent glass with good lighting performance cannot be selected as servere cold region, and low heat reflection should be selected, such as thermal reflective coated hollow glass and Low-E hollow glass. To meet the needs of different buildings in different regions, select glass with corresponding heat transfer coefficient and shading coefficient.
Selection of accessories
"Hardware accessories are the heart of doors and windows, not supporting roles." If a person has developed limbs and looks good in appearance, isn't it a loser if his heart doesn't work? The same is true for doors and windows. Hardware accessories play a very important role in energy-saving doors and windows. They are not only closely related to the air tightness, water tightness and wind pressure resistance of doors and windows, but also play a very important role in safety and other performance.
Correct assembly
These points are the requirements of several groups of components of doors and windows. Reasonable selection of components is very important, and the correct combination of various components into a system is a perfect energy-saving door and window, so it has the strength, experienced door and window brands are also crucial.
The real energy-saving doors and windows should not only adopt the perfect combination of good profiles, glass and accessories and good materials, but also be the element of systematic comprehensive evaluation.


