With the gradual progress of building energy-saving consciousness, the thermal insulation function of transparent part of glass has become the focus of our attention. Currently, the ways to improve the thermal insulation function of glass include: 1) selecting high-functional Low-E glass; 2) adding the number of glass and cavity, such as adding double glass single cavity to three glass two cavities, or even four glasses and three chambers; 3) change the gas composition in the cavity, such as filling argon/argon gas, Argon Krypton mixture and other inert gases; 4) withdraw the gas and make it into vacuum glass; 5) add hollow glass inner cavity thickness and so on.
The main point of this article is to introduce Why Argon should be filled inside hollow glass? What effect can it play?
How does building glass heat transfer?
First of all, let's take a look at how the construction of glass transfers heat. As shown in Figure 1, the heat transfer through the transparent part of glass includes two methods, namely temperature difference heat transfer and solar radiation heat transfer. Due to different heat transfer methods, the corresponding technical methods adopted to improve the quality and function of glass are also different.
Temperature difference heat transfer is mainly controlled by decreasing the heat transfer coefficient K of glass, while solar radiation heat transfer is mainly controlled by conditioning the total solar energy transmission ratio g and the total infrared heat energy transmission ratio gIR.
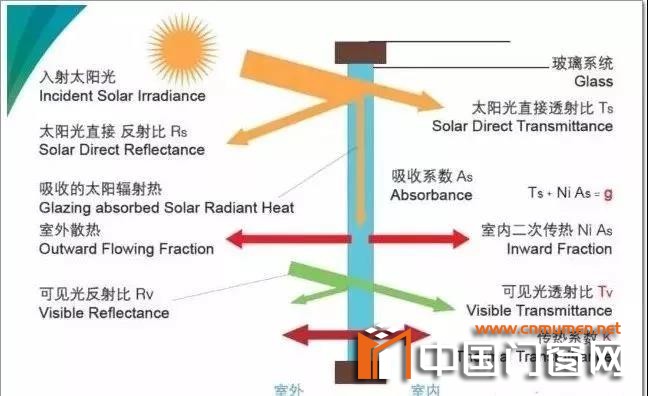
Figure 1 basic schematic diagram of heat transfer
Influencing Factors of heat transfer coefficient K value of hollow glass
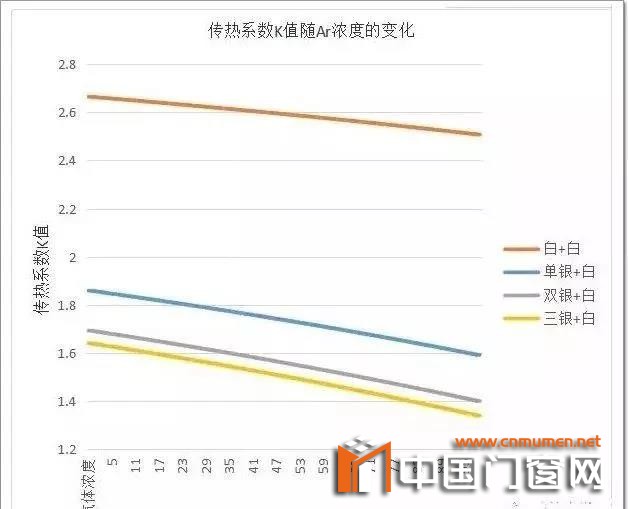
fig. 2 Schematic diagram of heat transfer mechanism of insulating glass temperature difference
As shown in Figure 2, to reduce the heat transfer coefficient of hollow glass, it is necessary to reduce heat radiation, convection heat transfer and heat conduction. Generally, single or multiple pieces of Low-E glass (single silver, double silver or three silver) are adopted., fill in inert gas, add the number of cavities or the thickness of the cavity. The main points of this article comment on the influence of argon filling on the heat transfer coefficient K value of glass.
Introduction to argon
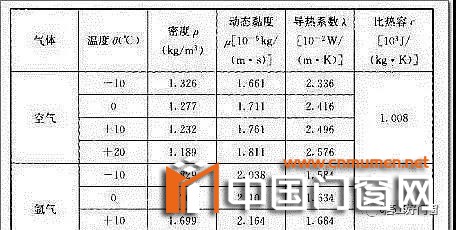
as we all know, argon is a kind of inert gas, which has the characteristics of colorless, tasteless and non-toxic, and has stability at the same time. In the air, its content accounts for about 1%. Compared with krypton and xenon, it is the most economical inert gas. The physical functions of the two are compared with those in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the density and dynamic viscosity of argon are higher than that of air, and the thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity are lower than that of air. Filling into the hollow glass can slow down the heat convection and heat conduction in the hollow glass, and then weaken the heat conduction ability of all the hollow glass, thus reducing the heat transfer coefficient K value.
How to calculate the thermal conductivity of different gases with different thickness? For more information, see Appendix A in JGJ 113 or 6.3 in JGJ/T 151.
Table 1 Comparison of argon and air characteristics
change of heat transfer coefficient K value after filling argon

fig. 3 the change of K value of double glass heat transfer coefficient with Ar concentration
It can be seen from Figure 3 that the heat transfer coefficient of the glass we analyzed obviously decreases with the addition of argon content. Taking single silver + white glass as an example, argon content decreased from 0 to 100%, heat transfer coefficient decreased from 1.86 to 1.59; Three Silver + white glass, heat transfer coefficient decreased from 1.64 to 1.34.
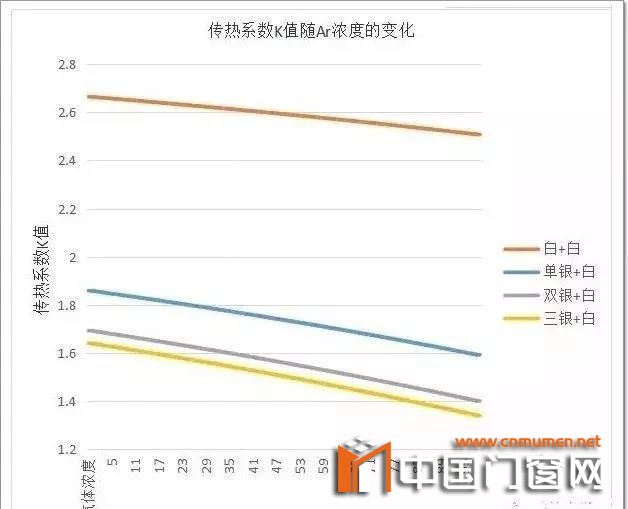
Fig. 4 Change of heat transfer coefficient K value with Ar concentration
it can be seen from Figure 4 that the heat transfer coefficient decreases obviously with the addition of argon content. Taking single silver + white glass + white glass as an example, the argon content is from 0 to 100%, and the heat transfer coefficient decreases from 1.36 to 1.17; Three Silver + white glass + white glass, the heat transfer coefficient decreases from 1.24 to 1.02.
Changes of shading coefficient SC and relative heating RHG after filling argon
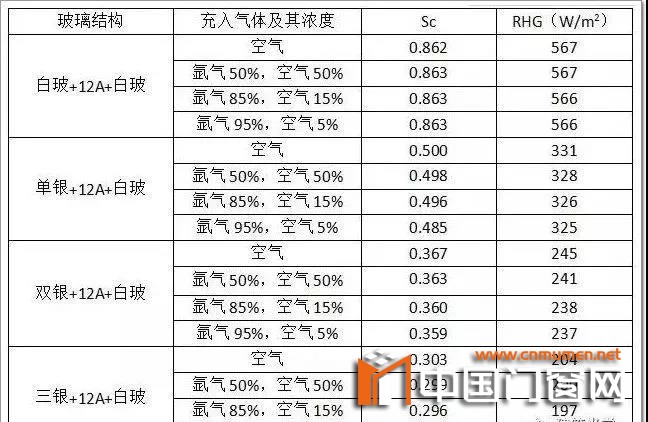
table 2 shows the changes of SC and relative heating RHG with gas composition of different glass structures for our reference.
Table 2 changes of SC and RHG with gas composition
conclusion:
from the analysis in this paper, it can be seen that whether the hollow glass cavity is filled with argon and the content of argon has a great influence on the heat transfer coefficient K value, and has a certain influence on the shading coefficient SC and relative heating RHG, however, the impact is slightly corrected. In addition, after being filled with inert gas, the Low-E membrane layer, especially the offline Low-E membrane, can be maintained better, making it more durable, and then extending the life of hollow glass. At the same time, the sound insulation function of glass filled with inert gas will also be improved.


 Figure 1 basic schematic diagram of heat transfer
Influencing Factors of heat transfer coefficient K value of hollow glass
Figure 1 basic schematic diagram of heat transfer
Influencing Factors of heat transfer coefficient K value of hollow glass
 fig. 2 Schematic diagram of heat transfer mechanism of insulating glass temperature difference
As shown in Figure 2, to reduce the heat transfer coefficient of hollow glass, it is necessary to reduce heat radiation, convection heat transfer and heat conduction. Generally, single or multiple pieces of Low-E glass (single silver, double silver or three silver) are adopted., fill in inert gas, add the number of cavities or the thickness of the cavity. The main points of this article comment on the influence of argon filling on the heat transfer coefficient K value of glass.
Introduction to argon
as we all know, argon is a kind of inert gas, which has the characteristics of colorless, tasteless and non-toxic, and has stability at the same time. In the air, its content accounts for about 1%. Compared with krypton and xenon, it is the most economical inert gas. The physical functions of the two are compared with those in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the density and dynamic viscosity of argon are higher than that of air, and the thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity are lower than that of air. Filling into the hollow glass can slow down the heat convection and heat conduction in the hollow glass, and then weaken the heat conduction ability of all the hollow glass, thus reducing the heat transfer coefficient K value.
How to calculate the thermal conductivity of different gases with different thickness? For more information, see Appendix A in JGJ 113 or 6.3 in JGJ/T 151.
Table 1 Comparison of argon and air characteristics
fig. 2 Schematic diagram of heat transfer mechanism of insulating glass temperature difference
As shown in Figure 2, to reduce the heat transfer coefficient of hollow glass, it is necessary to reduce heat radiation, convection heat transfer and heat conduction. Generally, single or multiple pieces of Low-E glass (single silver, double silver or three silver) are adopted., fill in inert gas, add the number of cavities or the thickness of the cavity. The main points of this article comment on the influence of argon filling on the heat transfer coefficient K value of glass.
Introduction to argon
as we all know, argon is a kind of inert gas, which has the characteristics of colorless, tasteless and non-toxic, and has stability at the same time. In the air, its content accounts for about 1%. Compared with krypton and xenon, it is the most economical inert gas. The physical functions of the two are compared with those in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the density and dynamic viscosity of argon are higher than that of air, and the thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity are lower than that of air. Filling into the hollow glass can slow down the heat convection and heat conduction in the hollow glass, and then weaken the heat conduction ability of all the hollow glass, thus reducing the heat transfer coefficient K value.
How to calculate the thermal conductivity of different gases with different thickness? For more information, see Appendix A in JGJ 113 or 6.3 in JGJ/T 151.
Table 1 Comparison of argon and air characteristics
 change of heat transfer coefficient K value after filling argon
change of heat transfer coefficient K value after filling argon
 Fig. 4 Change of heat transfer coefficient K value with Ar concentration
it can be seen from Figure 4 that the heat transfer coefficient decreases obviously with the addition of argon content. Taking single silver + white glass + white glass as an example, the argon content is from 0 to 100%, and the heat transfer coefficient decreases from 1.36 to 1.17; Three Silver + white glass + white glass, the heat transfer coefficient decreases from 1.24 to 1.02.
Changes of shading coefficient SC and relative heating RHG after filling argon
table 2 shows the changes of SC and relative heating RHG with gas composition of different glass structures for our reference.
Table 2 changes of SC and RHG with gas composition
Fig. 4 Change of heat transfer coefficient K value with Ar concentration
it can be seen from Figure 4 that the heat transfer coefficient decreases obviously with the addition of argon content. Taking single silver + white glass + white glass as an example, the argon content is from 0 to 100%, and the heat transfer coefficient decreases from 1.36 to 1.17; Three Silver + white glass + white glass, the heat transfer coefficient decreases from 1.24 to 1.02.
Changes of shading coefficient SC and relative heating RHG after filling argon
table 2 shows the changes of SC and relative heating RHG with gas composition of different glass structures for our reference.
Table 2 changes of SC and RHG with gas composition
 conclusion:
from the analysis in this paper, it can be seen that whether the hollow glass cavity is filled with argon and the content of argon has a great influence on the heat transfer coefficient K value, and has a certain influence on the shading coefficient SC and relative heating RHG, however, the impact is slightly corrected. In addition, after being filled with inert gas, the Low-E membrane layer, especially the offline Low-E membrane, can be maintained better, making it more durable, and then extending the life of hollow glass. At the same time, the sound insulation function of glass filled with inert gas will also be improved.
conclusion:
from the analysis in this paper, it can be seen that whether the hollow glass cavity is filled with argon and the content of argon has a great influence on the heat transfer coefficient K value, and has a certain influence on the shading coefficient SC and relative heating RHG, however, the impact is slightly corrected. In addition, after being filled with inert gas, the Low-E membrane layer, especially the offline Low-E membrane, can be maintained better, making it more durable, and then extending the life of hollow glass. At the same time, the sound insulation function of glass filled with inert gas will also be improved.